Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kawano, Takahiro*; Mizuta, Naoki; Ueta, Shohei; Tachibana, Yukio; Yoshida, Katsumi*
JAEA-Technology 2023-014, 37 Pages, 2023/08
Fuel compact for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) is fabricated by calcinating a matrix consisting of graphite and binder with the coated fuel particle. The SiC-matrixed fuel compact uses a new matrix made of silicon carbide (SiC) replacing the conventional graphite. Applying the SiC-matrixed fuel compact for HTGRs is expected to improve their performance such as power densities. In this study, the sintering conditions for applying SiC as the matrix of fuel compacts for HTGR are selected, and the density and thermal conductivity of the prototype SiC are measured.
Endo, Takashi*; Tachi, Yukio; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Terashima, Motoki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 20(1), p.9 - 22, 2021/03
Evaluation method of colloid diffusion and filtration in compacted bentonites was developed using dendrimers. Diffusion and filtration behavior of PAMAM dendrimers with the size of 5.7 7.2nm was investigated by the through-diffusion experiment in bentonite compacted to 0.8 Mg/m
7.2nm was investigated by the through-diffusion experiment in bentonite compacted to 0.8 Mg/m and saturated with 0.005
and saturated with 0.005 0.5mol/L NaCl. Effective diffusivities (De) and filtration ratios (Rf) of dendrimers were determined from the breakthrough curves and the depth profiles in compacted bentonite, respectively. The De values of negatively charged dendrimer increased when porewater salinity increased and dendrimer size decreased as influenced by anion exclusion effect in negatively charged clay surfaces. The Rf values increased when porewater salinity decreased and dendrimer size increased, demonstrating significant fractions of dendrimer were filtered by narrow pores in complex pore networks. These trends consistent with the previous studies emphasize the validity of the evaluation method using dendrimer.
0.5mol/L NaCl. Effective diffusivities (De) and filtration ratios (Rf) of dendrimers were determined from the breakthrough curves and the depth profiles in compacted bentonite, respectively. The De values of negatively charged dendrimer increased when porewater salinity increased and dendrimer size decreased as influenced by anion exclusion effect in negatively charged clay surfaces. The Rf values increased when porewater salinity decreased and dendrimer size increased, demonstrating significant fractions of dendrimer were filtered by narrow pores in complex pore networks. These trends consistent with the previous studies emphasize the validity of the evaluation method using dendrimer.
Ueta, Shohei; Mizuta, Naoki; Sasaki, Koei; Sakaba, Nariaki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Yan, X.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00571_1 - 19-00571_12, 2020/06
JAEA has been progressing to design HTGR fuels for not only small-type practical HTGRs but also VHTR proposed in GIF which can be utilized for various purposes with high-temperature heat at 750 to 950  C. To increase economy of these HTGRs, JAEA has been upgrading the design method for the HTGR fuel, which can maintain their integrities at the burnup of three to four times higher than that of the conventional HTTR fuel. Design principles and specifications of various concepts of the high burnup HTGR fuels designed by JAEA are reported. As the latest results on post-irradiation examinations of the high burnup HTGR fuel progressing in a framework of international collaboration with Kazakhstan, irradiation shrinkage rate of the fuel compact as a function of fast neutron fluence was obtained at around 100 GWd/t. Furthermore, the future R&Ds needed for the high burnup HTGR fuel are described based on these experimental results.
C. To increase economy of these HTGRs, JAEA has been upgrading the design method for the HTGR fuel, which can maintain their integrities at the burnup of three to four times higher than that of the conventional HTTR fuel. Design principles and specifications of various concepts of the high burnup HTGR fuels designed by JAEA are reported. As the latest results on post-irradiation examinations of the high burnup HTGR fuel progressing in a framework of international collaboration with Kazakhstan, irradiation shrinkage rate of the fuel compact as a function of fast neutron fluence was obtained at around 100 GWd/t. Furthermore, the future R&Ds needed for the high burnup HTGR fuel are described based on these experimental results.
Ueta, Shohei; Mizuta, Naoki; Sasaki, Koei; Sakaba, Nariaki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Yan, X.
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/05
JAEA has been progressing to design HTGR fuels for not only small-type practical HTGRs but also VHTR proposed in GIF which can be utilized for various purposes with high-temperature heat at 750 to 950  C. To increase economy of these HTGRs, JAEA has been upgrading the design method for the HTGR fuel, which can maintain their integrities at the burnup of three to four times higher than that of the conventional HTTR fuel. Design principles and specifications of various concepts of the high burnup HTGR fuels designed by JAEA are reported. As the latest results on post-irradiation examinations of the high burnup HTGR fuel progressing in a framework of international collaboration with Kazakhstan, irradiation shrinkage rate of the fuel compact as a function of fast neutron fluence was obtained at around 100 GWd/thm. Furthermore, the future R&Ds needed for the high burnup HTGR fuel are described based on these experimental results.
C. To increase economy of these HTGRs, JAEA has been upgrading the design method for the HTGR fuel, which can maintain their integrities at the burnup of three to four times higher than that of the conventional HTTR fuel. Design principles and specifications of various concepts of the high burnup HTGR fuels designed by JAEA are reported. As the latest results on post-irradiation examinations of the high burnup HTGR fuel progressing in a framework of international collaboration with Kazakhstan, irradiation shrinkage rate of the fuel compact as a function of fast neutron fluence was obtained at around 100 GWd/thm. Furthermore, the future R&Ds needed for the high burnup HTGR fuel are described based on these experimental results.
Mizuta, Naoki; Aoki, Takeshi; Ueta, Shohei; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Yan, X.
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2019/05
Enhancement of safety and cooling performance of fuel elements are desired for a commercial High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR). Applying sleeveless fuel elements and dual side directly cooling structures with oxidation resistant SiC-matrix fuel compact has a possibility of improving safety and cooling performance at the pin-in-block type HTGR. The irradiated effective thermal conductivity of a fuel compact is an important physical property for core thermal design of the pin-in-block type HTGR. In order to discuss the irradiated effective thermal conductivity of the SiC-matrix fuel compact which could improve the cooling performance of the reactor, the maximum fuel temperature during normal operation of the pin-in-block type HTGR with dual side directly cooling structures are analytically evaluated. From these results, the desired irradiated thermal conductivity of SiC matrix are discussed. In addition, the suitable fabrication method of SiC-matrix fuel compact is examined from viewpoints of the sintering temperature, the purity and the mass productivity.
Takahashi, Hiroaki*; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 168, p.211 - 222, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:47.52(Chemistry, Physical)Microstructural and mass transport properties of compacted Na- and Cs-montmorillonites with different swelling properties were investigated by combining 3D microstructure analysis using nanofocus X-ray CT and diffusion measurement of HDO. The X-ray CT observations indicated that macropores in the dry state of compacted Na-montmorillonite are filled with gel phases, and the grain sizes of clay particles shifted toward smaller values through the saturation and swelling processes. By contrast, no gel phase and no decrease in the grain and pore volumes were observed for saturated Cs-montmorillonite. The geometrical factors of the macropores including tortuosity and geometric constrictivity of saturated Cs-montmorillonite determined by the X-ray CT was consistent with the corresponding values derived in the HDO diffusion test. In the case of Na-montmorillonite, the larger differences between the geometric factors evaluated by the X-ray CT and the diffusion tests can be explained by the electrostatic constrictivity factor and the additional geometrical factors in gel phase and interlayer that are smaller than the detection limit of the X-ray CT.
Ishikawa, Hirotaku*; Kai, Tetsuya; Sato, Hirotaka*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(2), p.221 - 227, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.89(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yotsuji, Kenji; Tachi, Yukio; Okubo, Takahiro*
CMS Workshop Lectures, Vol.21, p.251 - 257, 2016/06
We have developed integrated sorption and diffusion model (ISD model) for assessment of diffusion parameters consistent with sorption processes in compacted bentonite. The ISD model gives consistent consideration to porewater chemistry, sorption and diffusion processes in compacted bentonite. The diffusion component based on the electric double layer theory and the homogeneous pore model in the ISD model accounts consistently for cation De overestimation and anion exclusion in narrow pores. The current ISD model can quantitatively account for diffusion of monovalent cations and anions, however, the model predictions disagree with diffusion data for multivalent cation and complex species. To improve the applicability of the model, it is necessary to consider the atomic level interactions between solute, solvent or clay mineral, and try that we apply the current ISD model to heterogeneous pore structure. In this study we try the application of the current ISD model to multiple pore structure. As results of numerical analysis of these models, the salinity dependence of effective diffusivity for the multi-pore model is comparatively smaller than that for the homogeneous pore model and the current diffusion model is improved.
 activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions
activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditionsSawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Mukai, Masayuki
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.267 - 278, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.47(Chemistry, Physical)The dependences of the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite on activity of OH (a
(a -) and temperature (T) were investigated. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite (
-) and temperature (T) were investigated. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite (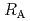 ) in compacted pure montmorillonite, which was formulized as
) in compacted pure montmorillonite, which was formulized as 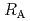 = 10
= 10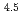 (a
(a -)
-)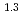 e
e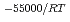 , was higher than that in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures:
, was higher than that in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures: 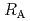 = 3500 (a
= 3500 (a -)
-)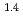 e
e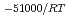 . The difference can be explained by considering the decrease in a
. The difference can be explained by considering the decrease in a - in the mixtures accompanied by dissolution of accessory minerals such as quartz and chalcedony. The dissolution rate model developed for pure montmorillonite is expected to be applied to bentonite mixtures if quantification of the decrease in a
- in the mixtures accompanied by dissolution of accessory minerals such as quartz and chalcedony. The dissolution rate model developed for pure montmorillonite is expected to be applied to bentonite mixtures if quantification of the decrease in a - is achieved somehow.
- is achieved somehow.
Okubo, Takahiro*; Ibaraki, Moe*; Tachi, Yukio; Iwadate, Yasuhiko*
Applied Clay Science, 123, p.148 - 155, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:74.44(Chemistry, Physical)The pore distribution of water-saturated compacted clay (Na-montmorillonite at 0.8 and 1.4 g/cm saturated by three salt concentrations) was evaluated using
saturated by three salt concentrations) was evaluated using  H NMR relaxometry and freezing point depression. The populations of interlayer water with four hydrated state and non-interlayer water were calculated from the assumed thresholds. The sample with lower density exhibits higher population of non-interlayer water up to 55%. Low-temperature
H NMR relaxometry and freezing point depression. The populations of interlayer water with four hydrated state and non-interlayer water were calculated from the assumed thresholds. The sample with lower density exhibits higher population of non-interlayer water up to 55%. Low-temperature  H NMR experiments in view of freezing point depression indicated that mesopore water in approximately 4 nm space observed in the calorimetric study was considered as non-interlayer water and the threshold temperature. The result showed that population of non-interlayer water by expected from freezing point depression agreed with
H NMR experiments in view of freezing point depression indicated that mesopore water in approximately 4 nm space observed in the calorimetric study was considered as non-interlayer water and the threshold temperature. The result showed that population of non-interlayer water by expected from freezing point depression agreed with  H NMR relaxometry within 10%. Correlation experiments between longitudinal (
H NMR relaxometry within 10%. Correlation experiments between longitudinal (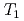 ) and transverse relation times (
) and transverse relation times (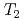 ) at -10
) at -10 C suggested that high-mobility bulk-like water molecules existed at a clay density of 1.4 g/cm
C suggested that high-mobility bulk-like water molecules existed at a clay density of 1.4 g/cm .
.
Tobita, Toru; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Otsu, Takuyo; Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 137(5), p.051405_1 - 051405_8, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:54.45(Engineering, Mechanical)We conducted a series of fracture toughness tests based on the Master curve method for several specimen size and shapes, such as 0.16T-CT, pre-cracked Charpy type, 0.4T-CT and 1T-CT specimens, in commercially manufactured 5 kinds of A533B class1 steels with different impurity contents and fracture toughness levels. The reference temperature ( ) values determined from the 0.16T-CT specimens were overall in good agreement with those determined from the 1T-CT specimens. The scatter of the 1T-equivalent fracture toughness values obtained from the 0.16T-CT specimens was equivalent to that obtained from the other larger specimens. The higher loading rate gave rise to a slightly higher
) values determined from the 0.16T-CT specimens were overall in good agreement with those determined from the 1T-CT specimens. The scatter of the 1T-equivalent fracture toughness values obtained from the 0.16T-CT specimens was equivalent to that obtained from the other larger specimens. The higher loading rate gave rise to a slightly higher  , and this dependency was almost the same for the larger specimens. We suggested an optimum test temperature on the basis of the Charpy transition temperature for determining
, and this dependency was almost the same for the larger specimens. We suggested an optimum test temperature on the basis of the Charpy transition temperature for determining  using the 0.16T-CT specimens.
using the 0.16T-CT specimens.
Kuwabara, Kazumichi; Sato, Toshinori; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Takayama, Yusuke
JAEA-Research 2015-005, 378 Pages, 2015/07
This report presents the results of following rock mechanical investigations conducted at the -500m Stage. (1) Laboratory tests using cores and block samples obtained at the -500m Stage. (2) In-situ stress measurement using Compact Conical-ended Borehole Overcoring (CCBO) method at the -500m Stage. (3) In-situ stress measurements using Differential Strain Curve Analysis(DSCA) method at the -500m Stage. (4) Development of rock mechanical model.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Tobita, Toru; Otsu, Takuyo; Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 2015 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2015) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2015/07
Fracture toughness evaluation by the Master Curve method using miniature compact tension (Mini-C(T)) specimens taken from the broken halves of surveillance Charpy specimens has been proposed. We performed finite element analysis (FEA) to examine the difference in constraint effect of the crack tip for the different size C(T) and precracked Charpy v-notch specimens. The constraint effect for Mini-C(T) specimens in terms of the T-stress and Q-parameter was similar to the larger C(T) specimens. To optimize the fatigue precracking conditions for the Mini-C(T) specimen fabrication, plastic zone distribution analysis was performed. We confirmed the fatigue precrack length and the availability of the mitigated crack shape for Mini-C(T). We also obtained the fracture toughness data for different sizes specimen. It was shown that To obtained from the Mini-C(T) specimens is in reasonably good agreement with that from others. We compared the fracture toughness data with T41J based fracture toughness curves proposed in recent study. All of the data were well enveloped by the proposed lower bound curve.
Ishii, Yasuyuki; Okubo, Takeru; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Saito, Yuichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 348, p.79 - 82, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Instruments & Instrumentation)Moriyama, Shinichi; Kajiwara, Ken*; Takahashi, Koji; Kasugai, Atsushi; Seki, Masami; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; JT-60 Team
Review of Scientific Instruments, 76(11), p.113504_1 - 113504_6, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:33.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)A compact antenna has been designed and fabricated to enable millimeter wave beam scan in the toroidal and the poloidal directions of the JT-60U Tokamak, for electron cyclotron heating (ECH) and current drive (ECCD) experiments. It consists of fast movable flat mirror mounted on the Tokamak vacuum vessel, and rotary focusing mirror attached at the end of the waveguide supported from outside of the vacuum vessel. This separate support concept enables compact structure in the shallow port (0.68 m  0.54 m
0.54 m  0.2m) sharing with a sub-port for an independent diagnostic system. The flat mirror is driven during a shot by a servo-motor with a 3 m long drive shaft to refuse influence of the high magnetic field to the motor. The focusing mirror is rotated by a simple mechanism with a push rod and an air cylinder. The antenna has been operated reliably for 3 years after small improvement in the rotary mechanism. It has been contributing ECH and ECCD experiments especially current profile control, in JT-60U.
0.2m) sharing with a sub-port for an independent diagnostic system. The flat mirror is driven during a shot by a servo-motor with a 3 m long drive shaft to refuse influence of the high magnetic field to the motor. The focusing mirror is rotated by a simple mechanism with a push rod and an air cylinder. The antenna has been operated reliably for 3 years after small improvement in the rotary mechanism. It has been contributing ECH and ECCD experiments especially current profile control, in JT-60U.
Higuchi, Hidekazu; Momma, Toshiyuki; Nakashio, Nobuyuki; Kozawa, Kazushige; Tohei, Toshio; Sudo, Tomoyuki; Mitsuda, Motoyuki; Kurosawa, Shigenobu; Hemmi, Ko; Ishikawa, Joji; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
The JAERI constructed the Advanced Volume Reduction Facilities(AVRF). The AVRF consists of the Waste Size Reduction and Storage Facilities(WSRSF) and the Waste Volume Reduction Facilities(WVRF). By operating the AVRF, it will be able to produce waste packages for final disposal and to reduce the amount of the low level solid wastes. Cutting installations for large wastes such as tanks in the WSRSF have been operating since June 1999. The wastes treated so far amount to 600 m and the volume reduction ratio is around 1/3. The waste volume reduction is carried out by a high-compaction process or melting processes in the WVRF. The metal wastes from research reactors are treated by the high-compaction process. The other wastes are treated by the melting processes that enable to estimate radioactivity levels easily by homogenization and get chemical and physical stability. The WVRF have been operating with non-radioactive wastes since February 2003 for the training and the homogeneity investigation in the melting processes. The operation with radioactive wastes will start in FY2005.
and the volume reduction ratio is around 1/3. The waste volume reduction is carried out by a high-compaction process or melting processes in the WVRF. The metal wastes from research reactors are treated by the high-compaction process. The other wastes are treated by the melting processes that enable to estimate radioactivity levels easily by homogenization and get chemical and physical stability. The WVRF have been operating with non-radioactive wastes since February 2003 for the training and the homogeneity investigation in the melting processes. The operation with radioactive wastes will start in FY2005.
Minehara, Eisuke
Hoshasen To Sentan Iryo Gijutsu, p.135 - 142, 2003/06
Medical applications of Free-Electron Lasers(FELs), especially the FEL driven by a superconducting rf linac, look very promising because of the compactness, high efficiency, high power capability, tunability, ultra-short pulse width and so on. Here, the linac-based FEL is explained briefly and discussed all about the remarkable features and the road maps near future. Finally, some possible and usable applications of the FELs will be introduced and discussed in the relationship with the features above.
Araki, Masanori; Sato, Shinichi*; Senda, Ikuo; Omori, Junji*; Shoji, Teruaki
Fusion Engineering and Design, 58-59, p.887 - 892, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ura, Tamaki*; Takamasa, Tomoji*; Nishimura, Hajime*; Aoki, Taro*; Ueno, Michio*; Maeda, Toshio*; Nakamura, Masato*; Shimazu, Shunsuke*; Tokunaga, Sango*; Shibata, Yozo*; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2001-049, 154 Pages, 2001/07
JAERI has studied on design and operation of a nuclear powered submersible research vessel, which will navigate under sea in the Arctic Ocean, as a part of the design study of advanced marine reactors. This report describes operation conditions and an operating system of the vessel those were discussed by the specialists of hull design, sound positioning, ship motions and oceanography, etc. The design conditions on ship motions for submersible vessels were surveyed considering regulations in our country, and ship motions were evaluated assuming the observation activities in the Arctic Ocean. A submarine transponder system and an on ice communication buoy system were examined as a positioning and communication system supposing the activity under ice. Procedures to secure safety of nuclear powered submersible research vessel were discussed based on the investigation of accidents. These results were reflected to the concept of the nuclear powered submersible research vessel, and subjects fto be settled in the next step were clarified.
Sawa, Kazuhiro; Tobita, Tsutomu*; Suzuki, Shuichi*; Yoshimuta, Shigeharu*; Oda, Takefumi*; Watarumi, Kazutoshi*
JAERI-Tech 99-077, p.41 - 0, 1999/11
no abstracts in English